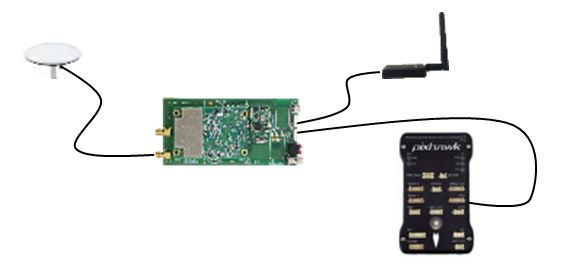
Precis-BX305 board can be integrated with autopilots. In this article, the connecting to Pixhawk flight control is used as an example. A cable is used to connect the COM1 port of Precis-BX305 board and the GPS port of the Pixhawk. It is noticed that the GPS port need a 6pin PicoBlade connector while the COM1 port is a 5pin PicoBlade connector. The pin definition of the Pixhawk GPS port is listed in Table 1.
With regarding to the power consumption, we recommend using external power sources. Please also pay attention to the baud rate setting of Pixhawk as the default baud rate of Precis-BX305 board is 115200. The Pixhawk can only recognize the NMEA sentence with GP NMEA talker. Incorrect NMEA talker configuration may cause connection failure.
Then you need to mount the GNSS antenna and tether the board on your vehicle. Please beware of following instructions when you mount the GNSS antenna to your drone.
■ Place the module on the outside of your vehicle (in an elevated position if appropriate) with a clear view of the sky
■ Distance the module from DC power wiring and the batteries by at least 10cm
Next step is setting up the Pixhawk with mission planner. Open Mission planner software and choose the right COM port on the top right corner. Choose 115200 as baud rate (default baud rate of Precis BX305 COM1 port). Then click ‘connect button’ on the right. Then the Precis-BX305 is recognized by mission planner if the GPS status becomes ‘3D Fix’.
Table 1. Pin definition of Pixhawk GPS port (from left to right)
|
Pin
|
Pin1
|
Pin2
|
Pin3
|
Pin4
|
Pin5
|
Pin6
|
|
Signal
|
VCC
|
TX
|
RX
|
CAN2 TX
|
CAN2 RX
|
GND
|
|
Voltage
|
+5V
|
+3.3V
|
+3.3V
|
+3.3V
|
+3.3V
|
GND
|
Figure 1. Demonstration of Integration with Pixhawk autopilot
If you have further questions, feel free to contact us to info@tersus-gnss.com or visit our official website www.tersus-gnss.com
Tersus Available on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn
We have created our Fan Page to keep you updated through the most used social network in the world. Come to "Like" or "Follow" us.
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/tersusgnss
Twitter: https://twitter.com/wwen0920
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/tersus-gnss
Comments
Post a Comment