Three Typical Situations of Earthwork Measurement
Tips for earthwork measurement under different circumstances with Tersus Oscar GNSS receiver and NUWA APP

Earthwork calculations are essential in many survey projects, but the complexity of measurement and calculations causes many new engineers headaches. In general, earthwork calculation is divided into two parts: excavation and filling, which can also be simply understood as volume and capacity calculation. The following are the Tips for using the Tersus Oscar GNSS receiver and NUWA App for earthwork measurement under different circumstances. The powerful earthwork calculation function of the NUWA app can calculate the result and quickly; you only need to import the survey points and then input the reference altitude.
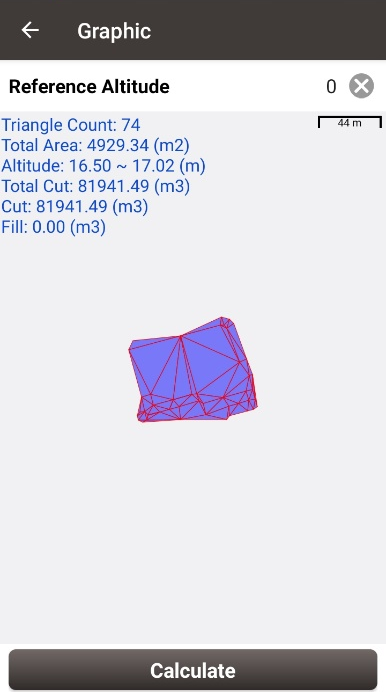
Notes for measurement:
When measuring points, we should measure as many points on the surface of the object as possible. The density of survey points needs to be strengthened in places where the terrain changes significantly, and the survey points can be relatively sparse in areas where the terrain is flat. In short, the more survey points, the closer the fitted shape is to the object itself, the more accurate the calculation results. Three typical situations are as below.
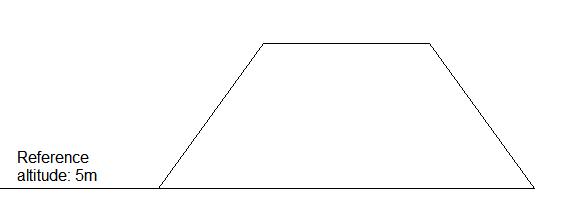
1. For the cross-section shown below, it's complete excavation, which can also be understood as the volume calculation, primarily seen in the measurement of sand and gravel, soil piles, wood, ore bodies, etc. We have to measure as many points on the surface of the object as possible. In the final calculation of the earthwork volume, enter the known reference altitude or the elevation of the object bottom, and the NUWA app can complete the calculation.
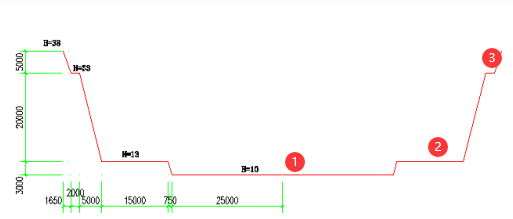
2. For the cross-section of the pit below, the pit's volume is calculated as a filling type or capacity calculation; we still need as many points as possible to ensure the measurement calculation accuracy. In the final calculation, we need to input the known reference altitude or measure the outside of the pit's elevation.
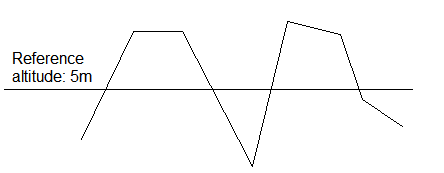
3. The topographic section in the figure below shows both filling and excavation mostly found inland leveling projects. In this case, we still need enough points to ensure the calculation result's accuracy; when calculating the final result, enter the reference altitude. The NUWA app will automatically calculate how much filling, how much excavation, and the total earthwork (fill and excavation).
4. Support
Should you need any technical support, please contact us without hesitation. support@tersu-gnss.com
Please check the input coordinate to make sure that it matches the actual coordinate. My supplied base coordinate is not accepted but the location coordinate. How to resolve this please
ReplyDeleteRegarding earthworks, your knowledge is quite helpful. Excavation involves much more than just creating a hole. To perform earthworks, one must move and remove rock and soil from a worksite in order to create an opening, trench, tunnel, or cavity. Every construction project needs excavation because it establishes a solid foundation for the project and offers a stable surface for the nearby property. When looking for quality service, Living Space provides earthworks Sunshine Coast service that is both on time and reasonably priced.
ReplyDelete