Change Battery without Base Shift
Oscar GNSS receiver “Change Battery” mode lets the surveyor free from re-configuring & base shift

Tersus Oscar GNSS receiver equips intelligent lithium batteries, which can detect electricity and display the power level intelligently. The built-in large capacity battery (7.4V 6400mAh) is detachable, and it supports up to 8 hours of fieldwork in 4G/3G/2G mode and Rover Radio mode.
If the surveyor is testing outdoors for a long time, the battery of the Oscar base station set up may be exhausted. Usually, he has to turn off the receiver, change a new battery, and restart it. After turning on, if he used the "Autostart" mode before, the Oscar GNSS receiver will start with new base coordinates. In this case, he has to do a "Base shift" to continue the previous project. If he used the "Manual start" mode with a known point before, the Oscar GNSS receiver would become a single mode. He has to reconfigure the base.
In response to this situation, we have developed a new feature-“Change Battery” mode. the Oscar receiver will automatically revert to its pre-shutdown state after the surveyor changes the battery without re-configuring the base or doing "Base shift." Let's take a look at how this mode works.
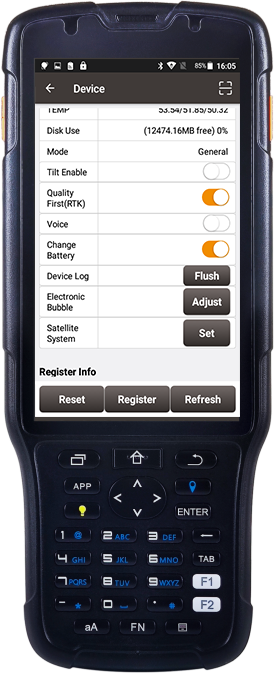
When you set an Oscar receiver as a base station and find the power light flickering after some time, it means you need to replace the battery as it is running low. At this point, you can connect to the Oscar base with the NUWA software, go to the "device" and turn on the "Change Battery" button, or turn on the mode in "Device Info--Change BAT" on the Oscar display. Then turn off the Oscar base, replace the battery, and restart it. Oscar receiver will automatically reconnect to the NUWA software after power-on. And you will find that it is still in base mode, and the base coordinates are the same as before power off. You can proceed to complete the measurement without having to reconfigure or do anything else.
Support
Should you need any technical support, please contact us without hesitation. support@tersu-gnss.com
Comments
Post a Comment