Complete the Base Shift Quickly
Few steps to complete the base shift
In ‘ Auto Start ’ mode for base station, if the base is moved, re-erected or restarted at an unknown point, base shift should be performed to ensure the points collected by the current base station is consistent with that before the base is moved or powered off. Briefly, find a known point, measure the coordinates of this point, then use this point to calculate the offset of the base shift, apply the base shift to all the survey points under the current base coordinates to make the reference coordinate system of the base remains the same as the previous base station.
The detailed steps are as follows:
1. Click [Base Shift] to enter the following interface, Figure 1 shows the calculation result for the base shift; Figure 2 shows the source of the base shift calculation.
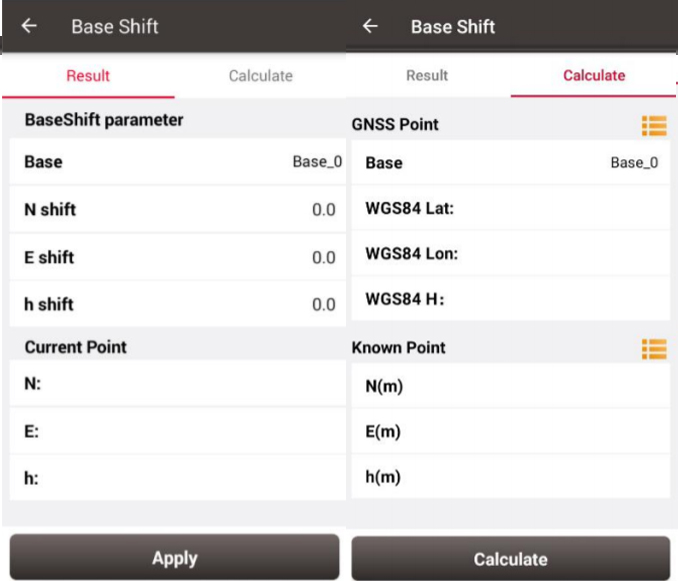
2. Click the list icon on the right of GNSS Point to select a survey point which is measured at the known point and click the list icon on the right of Known Point to select a known point in the control point library (details of control point refers to section 2.4 Point).
3. Click [Calculate] and the base shift is calculated automatically.
4. Click [Apply] to apply the base shift to all the points surveyed and to be surveyed under the current base station.
At this time, select the base point in the survey point library to view the details. It can be found that the current NEh shift amount is recorded in the base point information, and the NEh coordinates of all the survey points under this base station change accordingly.
If you need to reset (cancel) the base shift, just enter [base shift], and manually modify the three parameters of north shift, east shift and height shift to 0. At this time, return to the survey point library to view the details of the base point. The NEh shift amount in the base point information is automatically changed to 0, and all survey points NEh coordinates under the base station are restored to the coordinates before the base shift.
Support
Should you need any technical support, please contact us without hesitation. support@tersu-gnss.com
Comments
Post a Comment