In Nuwa app, if you want to stake out a line, there are two forms.
First form: after creating a line to be staked out, stake out to the stakes on the line or the offset line according to the entered stakeout interval.
Click [Line] -> [Staking Line] to enter the staking line library. Click [Add] and we use two points to determine a line. Enter the Start Mileage, turn on Point On Line Staking, enter Stakeout Interval and Offset shown as below.
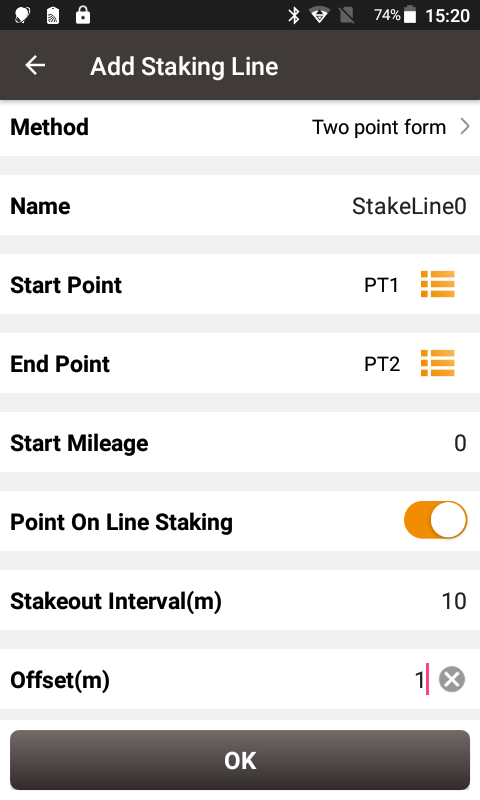
Start Mileage is a definition of the mileage given to the starting point of the line to determine the mileage value of other stakes on this line. Interval is used to determine how much distance to stake out a stake. For example, a stake is staked every 10m here, hence a line has a total length of 140.45m and a total of 16 stakes. Offset is the offset of the stake from the line. Of course, offset can be zero. When offset is 1, we consider that the stake is 1m to the right of the line forward direction.
Select this line for line stakeout. The first point is the stake point 1m to the right of the starting point. The second point is the stake point of 1m to the right of 10m on the line, and so on.
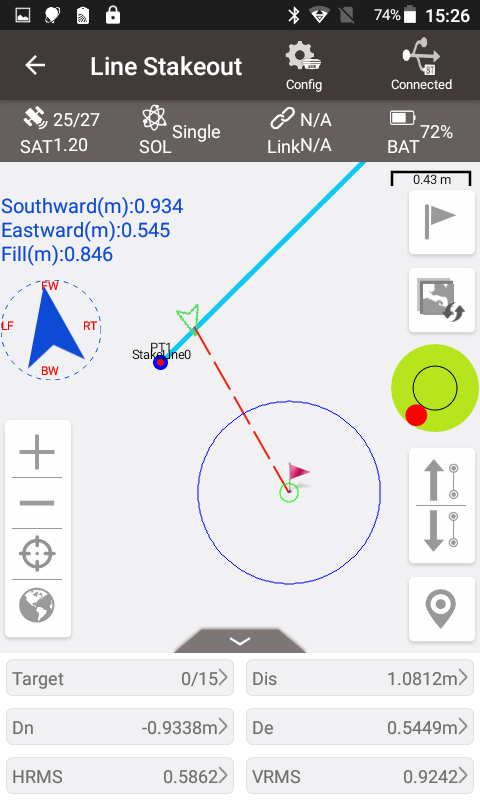
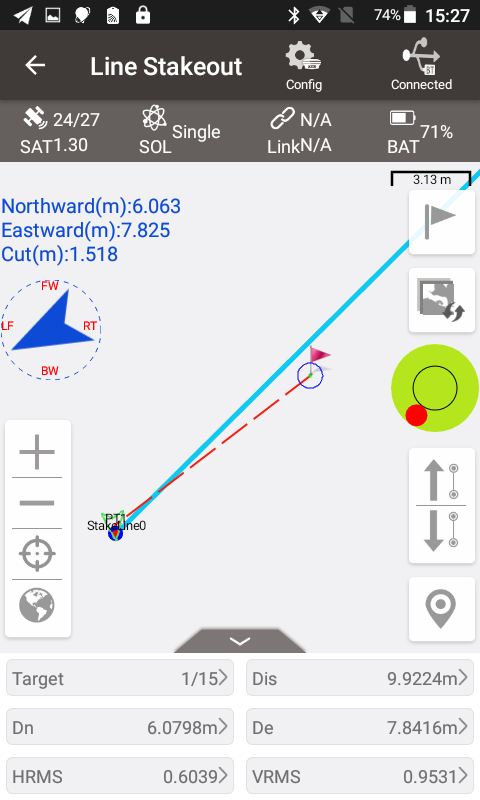
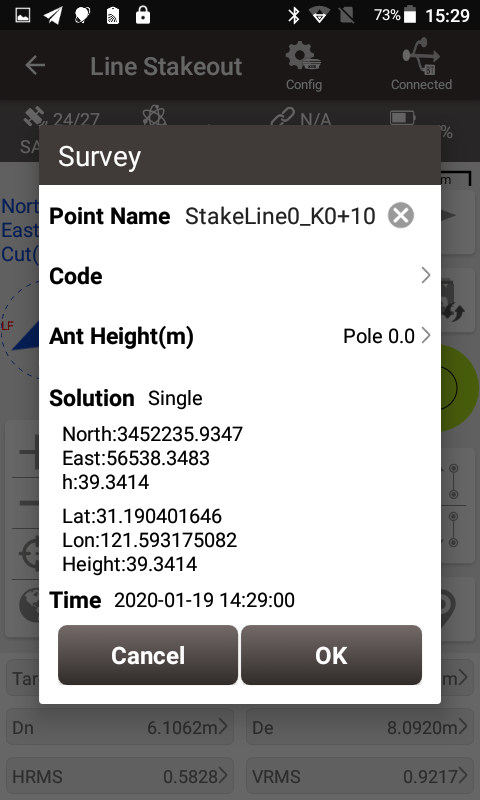
Using the up arrow and down arrow buttons, you can manually select the stakes to stake out. After stakeout points are collected, the software defaults the point name to the linename_stake mileage, for example the stake point at 10m on the line is named as StakeLine0_K0+10.
Second form: after creating a line to be staked, stake out to the vertical point on the line. The definition of the vertical point is: draw a vertical line to the line to be staked out passing the current position, and the point where the vertical line intersects with the line to be staked out is the vertical point.
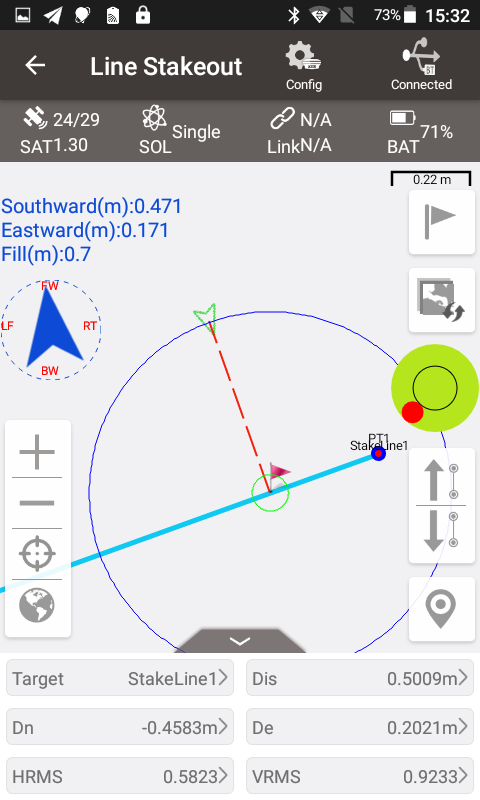
Obviously, as the current position changes, the vertical point will also move. This line staking method expresses that if you start from the current position, you can reach the position on the line to be staked as soon as possible.
Would you explain how to insert a * .dxf file into a project and how to trace it directly from the screen
ReplyDeleteHi, sorry for the late reply. We are working on inserting the DXF file as a base map on the screen, which will be implemented in the next version. You can download the Nuwa app from Google Play or at our website: https://www.tersus-gnss.com/software/oscar-receiver. We will upload the next release after comprehensive tests.
DeleteCan you stake out a line directly from the dxf drawing?
ReplyDelete